Table of Contents
Sleep deprivation is a big problem in the United States. About 20% of U.S. adults sleep less than five hours a night. This is way less than the seven hours they need.
Not getting enough sleep does more than just make you tired. It can really hurt your health and how well you do at work. People who don’t sleep well are more likely to get serious health problems. These include heart issues, diabetes, and a weak immune system.
It’s important to understand why we don’t sleep enough. This affects our work and how happy we are. Not sleeping well can mess up almost every part of our lives.
This article will look at why we don’t sleep enough and how to fix it. We’ll share tips to help you sleep better and feel healthier.
Quick Picks: Best aids to improve your sleep
[lasso id=”34″ link_id=”376″ type=”table”]
1 Understanding Sleep Deprivation: Definition and Basics
Sleep is key to our health, but many in the U.S. don’t get enough. About 1 in 3 adults say they don’t sleep well each day. This shows a big problem with not getting enough sleep in the country.

Experts say sleep deprivation and sleep insufficiency are different. Sleep deprivation means not sleeping at all one night. Sleep insufficiency is when you don’t sleep enough over time.
Types of Sleep Insufficiency
- Acute sleep insufficiency: Short-term lack of sleep
- Chronic sleep insufficiency: Long-term not enough sleep
- Intermittent sleep insufficiency: Sleep patterns that change a lot
Difference Between Sleep Deprivation and Insomnia
Insomnia is a sleep disorder that makes it hard to fall or stay asleep. Sleep deprivation is when you don’t get enough sleep in total. About 40% of adults feel very tired during the day, showing a big sleep problem.
Normal Sleep Requirements by Age
How much sleep we need changes as we get older. The CDC gives clear advice on how much sleep is best:
| Age Group | Recommended Sleep Hours |
|---|---|
| 0-3 months | 14-17 hours |
| 4-12 months | 12-16 hours (including naps) |
| 1-2 years | 11-14 hours (including naps) |
| 3-5 years | 10-13 hours (including naps) |
| 6-12 years | 9-12 hours |
| 13-18 years | 8-10 hours |
| 18-60 years | 7 or more hours |
“Sleep is not a luxury, it’s a necessity for optimal health and performance.” – Sleep Research Institute
Knowing how much sleep we need helps us spot sleep problems early. This can keep our health and happiness on track.
2 The Science Behind Sleep Cycles
Sleep is a complex process that helps our bodies and minds recover. It involves cycles that last about 90 to 120 minutes. Most people go through four to six cycles in eight hours of sleep.
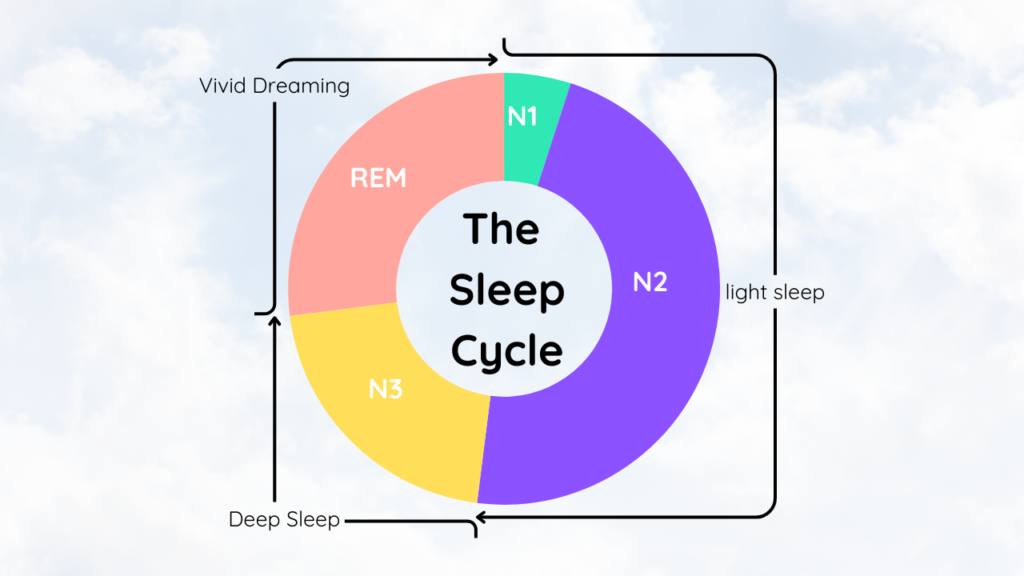
Sleep cycles have two main phases: non-REM (NREM) and REM sleep. The NREM phase has three stages, each with its own features:
- Stage 1 (N1): A light sleep lasting 1-5 minutes, representing the transition from wakefulness to sleep
- Stage 2 (N2): A deeper sleep stage where heart rate slows and body temperature drops
- Stage 3 (N3): Deep sleep crucial for physical recovery and restoration
REM sleep happens about 90 minutes after falling asleep. It’s when brain activity increases and dreams become vivid. The body is paralyzed, but the brain is busy processing information and memories.
“Sleep is the golden chain that binds health and our bodies together.” – Thomas Dekker
| Sleep Stage | Duration | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 (N1) | 1-5 minutes | Light sleep, easy to wake |
| Stage 2 (N2) | 10-60 minutes | Slower heart rate, decreased body temperature |
| Stage 3 (N3) | 20-40 minutes | Deep sleep, physical restoration |
| REM Sleep | 10-60 minutes | Dreaming, memory consolidation |
Knowing about sleep cycles shows how vital quality sleep is. Disruptions can cause sleep deprivation, affecting our health and mind.
3 Common Signs of Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation affects millions in the U.S. It’s estimated that 50 million to 70 million adults don’t get enough sleep. This lack of sleep impacts their health and daily life.

Spotting sleep deprivation symptoms early is key. It helps avoid serious health issues. Knowing how fatigue and brain fog show up is important for staying healthy.
Physical Symptoms
The body shows many signs of sleep deprivation:
- Persistent daytime drowsiness
- Frequent yawning
- Weakened immune system
- Increased sensitivity to pain
- Unintentional microsleeps
Mental and Emotional Indicators
Sleep deprivation affects the mind and emotions in many ways:
- Reduced concentration
- Memory problems
- Mood swings
- Increased anxiety
- Decreased emotional regulation
“Sleep is the golden chain that binds health and our bodies together.” – Thomas Dekker
Behavioral Changes
People without enough sleep often change their behavior:
- Reduced social interactions
- Impaired decision-making
- Slower reaction times
- Decreased work performance
- Increased risk-taking behaviors
Spotting these signs early can prevent long-term health complications and improve overall quality of life.
4 Lack of Sleep: Primary Causes and Risk Factors

Sleep problems affect millions of Americans every day. Studies show that 50 to 70 million adults have sleep disorders. This shows how common sleep issues are.
Many lifestyle choices can lead to not getting enough sleep:
- Irregular sleep schedules
- High-stress work environments
- Inconsistent sleep patterns
- Poor sleep hygiene
- Extended screen time before bed
Work can also hurt your sleep. About 20 percent of workers do shift work. There’s been a 24 percent rise in early morning work in the last decade.
“Sleep is not a luxury, it’s a biological necessity.” – Dr. Matthew Walker, Sleep Researcher
There are several risk factors for sleep disorders:
- Chronic stress
- Medical conditions
- Medication side effects
- Environmental disruptions
- Age-related changes
Sleep is key to our health. Not getting enough sleep can lead to serious health problems. These include:
| Health Condition | Risk Correlation |
|---|---|
| Obesity | High |
| Diabetes | Significant |
| Cardiovascular Disease | Elevated |
| Depression | Strong |
Understanding these sleep disruption causes is the first step toward improving sleep quality and overall health.
5 Impact on Cognitive Function and Performance
Sleep deprivation is a big challenge for our brains. Without enough sleep, our brain’s functions suffer. This leads to problems with daily tasks and making decisions.

Memory and Learning Challenges
Sleep is key for remembering things. Studies show that not enough sleep messes with how we remember and learn. People who don’t sleep well often find it hard to:
- Keep information in their memory
- Create new memories
- Learn new things
“Sleep is the golden chain that binds health and our bodies together.” – Thomas Dekker
[lasso id=”1671″ link_id=”233″ ref=”amzn-bronson-ginkgo-biloba-extra-strength-supports-brain-function-memory-support-360-vegetarian-capsules”]
Decision-Making Abilities
Not sleeping well hurts our ability to make decisions. Research shows that people who don’t sleep well:
- Think slower
- Reason less logically
- Make riskier choices
Reaction Time and Alertness
Not getting enough sleep makes us slower to react and less alert. Experts say sleep loss is like being drunk. Our reaction times slow down a lot, and our judgment gets worse.
| Sleep Duration | Cognitive Performance Impact |
|---|---|
| 4-5 hours | 25% reduction in cognitive function |
| Less than 4 hours | 50% reduction in reaction time |
Knowing how sleep affects our brains shows why we need to sleep well. It’s essential for our mental sharpness.
6 Physical Health Consequences

Not getting enough sleep can lead to serious health problems. Our bodies need sleep to stay healthy. Without it, we face many health risks.
“Sleep is not a luxury, it’s a biological necessity for survival and optimal health.” – National Sleep Foundation
Some big health risks from not sleeping enough include:
- Increased cardiovascular risks, including higher chances of heart attack and stroke
- Compromised immune function, reducing the body’s ability to fight infections
- Metabolic disorders leading to potential weight gain and obesity
- Elevated blood pressure and potential development of hypertension
Heart problems are a big worry with not enough sleep. Studies show that people who sleep less than 7 hours are more likely to have heart issues.
| Sleep Duration | Health Risk Increase |
|---|---|
| Less than 6 hours | 48% higher cardiovascular risk |
| 6-7 hours | 25% increased health complications |
| Recommended 7-9 hours | Optimal health protection |
Not sleeping enough hurts our immune system a lot. It messes with the production of important immune cells. This makes us more likely to get sick and can make vaccines less effective.
Prioritizing sleep is not just about feeling rested—it’s a fundamental strategy for protecting long-term physical health and preventing chronic disease.
7 Mental Health and Emotional Well-being
Sleep is key to keeping our minds healthy and emotions in check. Studies show a strong link between sleep and our mental state. They find that bad sleep habits can lead to mood issues and emotional ups and downs.

Depression and Anxiety Links
The link between sleep and mental health is complex. Research shows:
- Over 300 million people worldwide suffer from depression
- Approximately 75% of individuals with depression experience insomnia symptoms
- Anxiety disorders affect an estimated 20% of adults and 25% of teenagers
“Sleep is the golden chain that binds health and our bodies together.” – Thomas Dekker
Mood Regulation Issues
Not getting enough sleep can mess with our emotions. Lack of sleep makes us more prone to mood swings and emotional instability.
| Sleep Duration | Mental Health Impact |
|---|---|
| Less than 7 hours | Increased risk of anxiety and depression |
| 7-9 hours | Optimal emotional processing and mood stability |
| More than 9 hours | Potential negative psychological effects |
Knowing how sleep affects our mental health helps us value rest. It’s a crucial part of staying mentally well.
8 Effects on Work and Professional Life

Sleep deprivation can really hurt your work life. Almost 30% of American workers sleep less than 6 hours a day. This makes it hard to succeed at work.
Not getting enough sleep leads to more accidents at work. It also makes people less alert and less sharp. Companies lose a lot of money, about $1,967 per employee each year.
“Sleep deprivation transforms workplace efficiency into a critical challenge for modern professionals.”
- Decreased cognitive functioning
- Increased error rates
- Reduced reaction times
- Higher risk of workplace incidents
Managers and business owners often don’t get enough sleep. About 40.5% of them sleep less than 6 hours a day. This affects their ability to make good decisions and do their job well.
| Sleep Duration | Workplace Productivity Impact |
|---|---|
| < 6 hours | Significant performance decline |
| 7-9 hours | Optimal workplace performance |
| Irregular sleep patterns | Increased work-related accidents |
Poor sleep quality can lead to many problems at work. It can make people perform worse, hurt relationships, and lead to unethical behavior. The cost of sleep deprivation at work is huge, about $136.4 billion a year in the U.S.
9 Impact on Personal Relationships and Social Life
Sleep deprivation affects more than just our health. It also impacts our personal relationships and social life. Lack of sleep can slowly damage how we connect with others.

The effects of sleep on relationships are huge. Studies show how not getting enough sleep changes how we interact with others:
- Nearly 50% of Americans feel lonely or left out.
- People who don’t sleep well are seen as less appealing to others.
- They struggle to understand emotions.
Communication Challenges
When we don’t get enough sleep, talking to others gets harder. Brain scans show less activity in areas for social interaction. This makes it tough to form deep connections.
“One night of poor sleep can fundamentally alter how we perceive and interact with others.”
Social Withdrawal Patterns
Not getting enough sleep leads to feeling isolated. People who don’t sleep well often:
- Interact less with others.
- See more threats in social situations.
- Keep a distance from people.
| Sleep Quality | Social Interaction Impact |
|---|---|
| Poor Sleep | Decreased social confidence |
| Good Sleep | Improved social engagement |
| Chronic Sleep Deprivation | High risk of social isolation |
It’s key to understand how sleep affects our social lives. Getting enough sleep is vital for strong, healthy relationships.
10 Sleep Deprivation and Safety Risks

Sleep deprivation is a big threat to public safety. It’s not just about personal health. Drowsy driving and workplace accidents are major concerns that need urgent action.
“One night of poor sleep can transform an alert professional into a potential safety hazard.” – Sleep Research Institute
The effects of not getting enough sleep are wide-ranging and serious. About 40% of adults say they fall asleep during the day at least once a month. This is a big problem in many areas of life.
- Drowsy driving causes many traffic accidents every year
- Workplace accidents go up by 50% when employees are tired
- Jobs like healthcare and transportation are at high risk
[lasso id=”1673″ link_id=”235″ ref=”amzn-lgi-driver-fatigue-alarm-3-in-1-inside-sleep-alarm-for-drivers-security-guards-nap-zapper-alarm-security-car-alarm-system-drivers-security-guards-anti-sleep-alarm-nap-alert”]
Shift workers are at a high risk, with 75% feeling tired on the job. Doctors and nurses are also at risk, with studies showing they make more mistakes when working long hours.
| Safety Risk Category | Percentage Affected | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Driving Performance | 40% | Increased accident probability |
| Workplace Accidents | 30% | Higher injury rates |
| Medical Error Rates | 25% | Compromised patient safety |
The dangers of not getting enough sleep are not just immediate. Long-term sleep problems can lead to serious health issues and lower brain function. This makes it a big public safety issue that needs a strong response.
11 Medical Diagnosis of Sleep Issues
Getting a sleep disorder diagnosis needs a full medical check-up and special tests. Sleep studies are key in finding health problems linked to sleep. These issues can really affect how well someone lives.

Doctors use many ways to figure out sleep disorders. Over 80 sleep disorders exist. So, it’s vital to use precise tests for the right treatment.
Sleep Studies and Assessments
Sleep studies are detailed tools for doctors to understand sleep patterns. These tests usually include:
- Polysomnography (overnight sleep monitoring)
- Actigraphy (tracking movement and sleep-wake cycles)
- Home-based sleep assessments
- Detailed patient history evaluation
Professional Evaluation Methods
Sleep experts do deep medical checks to find sleep disorders. The process often includes:
- Comprehensive patient interview
- Review of sleep patterns and habits
- Assessment of daytime functioning
- Physical examination
- Potential referral for specialized testing
*”Accurate sleep disorder diagnosis is the first step toward effective treatment and improved quality of life.”*
About 50-70 million US adults have sleep disorders. This shows how crucial professional medical checks are. Signs like taking more than 30 minutes to fall asleep or frequent nighttime awakenings might mean a sleep disorder needs doctor’s care.
12 Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Changes

Improving sleep quality doesn’t always need medical help. Natural remedies and lifestyle changes can greatly improve your sleep. The CDC says adults should sleep at least 7 hours a night. Yet, nearly 19% of Americans find it hard to do this.
“Sleep is the golden chain that binds health and our bodies together.” – Thomas Dekker
Effective natural sleep aids can change your bedtime routine. Here are some useful tips:
- Practice daily meditation for stress reduction
- Engage in moderate exercise for 20-30 minutes
- Create a consistent sleep schedule
- Limit caffeine intake 6 hours before bedtime
Lifestyle changes are important for better sleep. Research shows certain actions can greatly improve sleep:
| Intervention | Potential Sleep Improvement |
|---|---|
| Daily Meditation | Significant reduction in insomnia symptoms |
| Magnesium Supplements | Improved sleep patterns after two months |
| Lavender Oil | Enhanced sleep for individuals with depression |
Natural methods like herbal teas, aromatherapy, music and relaxation can help too. Remember, consistent implementation is key to achieving lasting improvements in sleep hygiene.
[lasso id=”10″ link_id=”236″ type=”table”]
If you’re still having trouble sleeping, talk to a healthcare professional. They can give you advice that fits your needs.
13 Medical Treatments and Interventions
When sleep problems last a long time, doctors have many ways to help. They can help you sleep better. Knowing about these options can help those who can’t sleep well.

Sleep medicine is a big help for sleep problems. In the U.S., millions of sleep aids are given out every year. Some common ones are:
- Eszopiclone
- Ramelteon
- Zolpidem tartrate
- Low-dose Doxepin
Prescription Medications
Medicines can help you sleep better for a short time. But, it’s important to only use them for a few weeks to avoid getting too used to them. Many people find it hard to find a medicine that works well for them.
Therapeutic Approaches
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a big help for sleep problems. Doctors often suggest it first. It works well for many people, helping them sleep better.
“Cognitive Behavioral Therapy offers a holistic approach to treating sleep disorders without the potential side effects of medication.” – Sleep Medicine Experts
Other ways to help include:
- Light therapy
- Yoga and meditation
- Sleep hygiene education
- Relaxation techniques
[lasso id=”8″ link_id=”237″ type=”table”]
It’s best to talk to a doctor to find the right treatment for you. With the right help, you can sleep better and feel better overall.
14 Prevention Strategies and Sleep Hygiene

Improving sleep is key for good health and happiness. To do this, we need to make our sleep space better. This means looking at our daily habits and bedtime routines.
Creating a consistent sleep routine is important. Here are some steps to follow:
- Maintain a regular sleep schedule
- Design a calming bedtime ritual
- Optimize bedroom conditions
- Manage daytime habits
“Sleep is the golden chain that binds health and our bodies together” – Thomas Dekker
Your sleep environment is very important. The perfect bedroom should be:
| Environmental Factor | Recommended Setting |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 65 degrees Fahrenheit |
| Lighting | Dark and minimal |
| Noise Level | Quiet or white noise |
Studies show that up to 70% of adults have sleep issues sometimes. By using the right sleep tips, we can sleep better and feel healthier.
Here are some tips for a good sleep routine:
- Turn off digital devices 1-2 hours before bed
- Don’t drink caffeine after 2 PM
- Stay active during the day
- Try stress-reducing activities like meditation
By focusing on a good sleep space and regular sleep habits, we can sleep better. This helps us stay healthy in the long run.
15 Long-term Health Implications

Chronic sleep deprivation has serious long-term health risks. It’s not just about feeling tired. Research shows it can harm your health and shorten your life if you don’t get enough sleep.
Not getting enough sleep affects many parts of your body. This can lead to serious health problems. Sleep is key to staying healthy and living a long life, studies show.
- Cardiovascular system deterioration
- Metabolic dysfunction
- Compromised immune response
- Neurological performance decline
- Increased psychological vulnerability
Studies show the dangers of not getting enough sleep:
| Health Risk | Potential Consequence |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Health | 48% higher risk of heart disease |
| Metabolic Function | 55% increased diabetes risk |
| Mental Health | 37% higher depression likelihood |
“Sleep is not a luxury—it’s a biological necessity for human survival and optimal functioning.” – Dr. Matthew Walker, Sleep Researcher
Neurological consequences are severe with too little sleep. Your brain can’t think as well, remember things, or clear out toxins.
The message is clear: sleep is crucial for your health. It helps prevent chronic diseases and keeps you healthy for years to come.
16 Conclusion
Sleep is key in our fast-paced world. In the U.S., 83.6 million adults sleep less than 7 hours a night. This shows how important good sleep is for our health.
Not getting enough sleep affects our bodies and minds. It impacts how well we perform and live our lives. This is a big public health issue.
Many Americans, 50 to 70 million, have trouble sleeping. Those who sleep less than six hours a night are at a higher risk of dying early. Improving sleep quality is essential for staying healthy.
It’s not just about choosing to sleep well. It’s about keeping ourselves healthy for the long term. Knowing how sleep, lifestyle, and health are connected helps us make better choices.
Fixing sleep problems needs a complete approach. We must understand how not enough sleep affects us. This includes bad thinking and health risks.
By improving sleep habits, we can do better in life. Good sleep hygiene, managing stress, and getting help when needed can make a big difference.
Investing in sleep is investing in ourselves. Research shows how sleep affects our overall health. Taking steps to improve sleep can lead to better health and a better life.
Lack of sleep is a serious issue that affects many Americans, contributing to both physical and mental health problems. The lack of sleep can lead to decreased productivity and increased risk of accidents at work.
Research shows that lack of sleep can significantly impair cognitive function and emotional stability. Individuals experiencing lack of sleep often suffer from mood swings and increased stress levels.
Chronic lack of sleep can contribute to serious health issues such as obesity and diabetes. Many people are unaware of how lack of sleep affects their overall health and well-being.
Understanding the causes of lack of sleep can help us address this critical issue effectively. It is crucial to recognize the signs of lack of sleep to mitigate its effects on our lives.
Recognizing the impact of lack of sleep on productivity is crucial for employers. By reducing lack of sleep, individuals can enhance their performance in various life areas.
Addressing lack of sleep is essential for maintaining healthy relationships and social interactions. Understanding how lack of sleep affects our daily lives can inspire positive changes.
Recognizing the importance of addressing lack of sleep can lead to improved overall health. Understanding lack of sleep can lead to healthier choices and improved well-being.
Adequate sleep is essential for overall health, especially in combating lack of sleep. Individuals should prioritize sleep hygiene to combat the effects of lack of sleep.
Making small lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the impact of lack of sleep. Identifying personal triggers of lack of sleep can guide individuals toward better sleep habits.
Strategies to combat lack of sleep include establishing a regular sleep routine and minimizing screen time before bed. Addressing lack of sleep through proper sleep hygiene can lead to significant health benefits.
Finding effective solutions for lack of sleep can improve both mental and physical health. Effectively addressing lack of sleep enhances both mental clarity and physical health.
Taking proactive steps to resolve lack of sleep can improve quality of life. By prioritizing sleep, we can reduce the long-term effects of lack of sleep on health.
Seeking professional help is essential in addressing chronic lack of sleep. Creating supportive environments can mitigate the effects of lack of sleep.
Utilizing community support can help individuals combat the detrimental effects of lack of sleep. Educational resources regarding lack of sleep can empower individuals to take action.
Community awareness programs can educate about the risks of lack of sleep. Effective communication regarding lack of sleep can help spread awareness.
Encouraging open discussions about lack of sleep can lead to healthier communities. Improving community resources for sleep can help combat the issue of lack of sleep.
Collective efforts in addressing lack of sleep can lead to significant public health improvements. Addressing lack of sleep will improve not only individual health but also community health.
Ultimately, understanding and resolving lack of sleep is essential for overall well-being.










